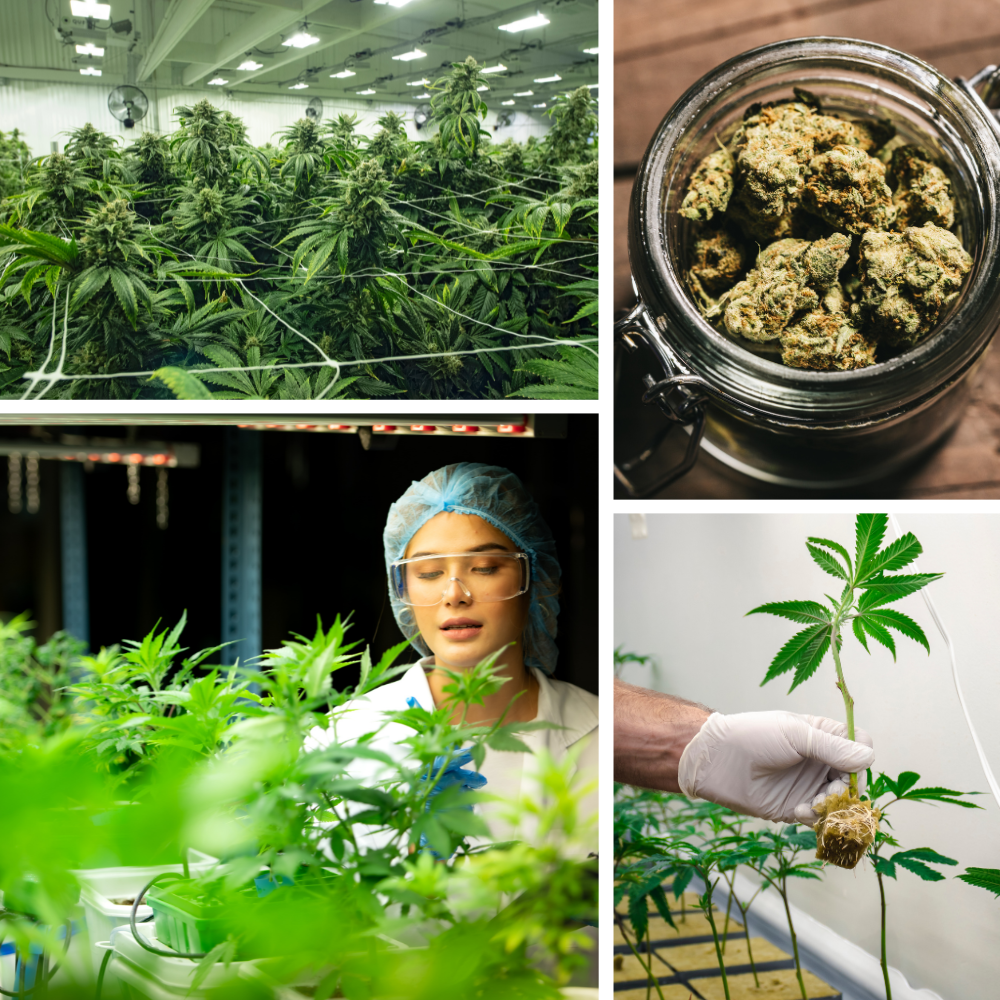
Green Clean: Elevate Your Cannabis Cultivation with Sodium Hypochlorite Sanitization
Bleach & Bud
In the meticulous world of cannabis cultivation, the sanctity of the grow room is paramount. A pristine environment is not just a matter of aesthetics; it’s the bedrock upon which thriving cannabis plants are nurtured. The introduction of contaminants, be they molds, pests, or pathogens, can transform a potential harvest of high-quality buds into a heartbreaking lesson in the importance of cleanliness.
As growers, you aren’t just farmers; y’all are the guardians of a closed ecosystem where every detail matters. It’s a place where the air must be as pure as the water that feeds the roots and where the surfaces gleam not out of vanity, but necessity. This article delves into the indispensable practice of grow room sanitization, a rigorous but rewarding ritual that safeguards your plants’ health, ensures your operation adheres to the highest standards, and, ultimately, secures the integrity of your yield.
Sanitization is the hero in the cultivation narrative. It’s the silent clean warrior that wards off invisible threats, ensuring that the only thing flourishing under your grow lights is the cannabis itself. Let’s embark on a thorough exploration of the best practices in grow room sanitization, ensuring your green sanctuary remains just that—a bastion of purity and excellence in the art and science of cannabis cultivation.
Why Kleaning with Sodium Hypochlorite is King for your Kush
Cannabis cultivation demands an environment where hygiene is not compromised. Among the myriad options for sanitization, Sodium Hypochlorite stands out as a champion for growers. Here’s why Sodium Hypochlorite is the cornerstone of cleanliness in the cultivation of cannabis, and the science behind its effectiveness.
The Rationale for Sodium Hypochlorite
1. Powerful Disinfectant Properties: Sodium Hypochlorite, the active ingredient in bleach, is a powerful broad-spectrum disinfectant. It’s adept at obliterating bacteria, fungi, viruses (and VIROIDS), ensuring that the myriad of potential pathogens are kept at bay. In the controlled ecosystem of a grow room, this level of thoroughness is non-negotiable.
2. Oxidizing Power: As an oxidizing agent, sodium hypochlorite attacks the proteins and lipids that make up harmful microorganisms. It essentially breaks down the cell walls, causing the internal structures of the microbes to become disrupted and die. This process is swift and unforgiving, making it incredibly effective for sanitization purposes.
3. Cost-Effective and Readily Available: For a commercial operation, economics matter. Sodium hypochlorite is not only effective, but it’s also cost-efficient. It is widely available and heavily stocked at Alliance Chemical so you don’t exhaust the operational budget, making it an economical choice for regular and large-scale sanitation efforts.
4. Easy to Use and Apply: Simplicity in the sanitization process is key to maintaining consistent cleanliness. Sodium hypochlorite solutions can be easily applied with sprayers, mops, or cloths, and they don’t require the procurement of specialized application equipment.
5. Quick Action: Time is of the essence in cultivation, and Sodium Hypochlorite acts rapidly to disinfect surfaces. This swift action minimizes downtime in the grow room, allowing for a more efficient sanitization process within the cultivation cycle.
-
 Sodium Hypochlorite 5.25%$20.00 – $2,295.00
Sodium Hypochlorite 5.25%$20.00 – $2,295.00 -
 Sodium Hypochlorite 12.5%$22.00 – $2,646.00
Sodium Hypochlorite 12.5%$22.00 – $2,646.00
The Mechanism of Sodium Hypochlorite
The mechanism by which Sodium Hypochlorite dispatches its cleaning duties is both straightforward and profound. Upon application, it releases hypochlorous acid, a potent molecule that penetrates the cell walls of microorganisms. Hypochlorous acid reacts with the cellular components, leading to the inactivation of vital cell functions and subsequent death of the pathogens. This chemical reaction occurs rapidly, ensuring that sanitization is accomplished in a timely manner.
For a grow room, where every surface can harbor potential threats to a crop, the need for a reliable and effective disinfectant is paramount. Sodium Hypochlorite’s ability to assure a broad-spectrum clean is invaluable, making it an indispensable ally in the constant battle against contamination.
In conclusion, Sodium Hypochlorite isn’t just a choice; it’s an essential weapon in the arsenal of cannabis cultivation. Its robust disinfectant properties, cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and rapid action make it the go-to for growers dedicated to ensuring the highest standards of cleanliness and plant health.
Efficacy of Sodium Hypochlorite Against Plant Viroid and Viruses
Sodium Hypochlorite, the active ingredient in bleach, is renowned for its broad-spectrum biocidal activity, making it an effective disinfectant against a wide array of pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This biocidal capability is due to its powerful oxidizing properties, which lead to the disruption of essential cell processes and structures within microbial cells.
When Sodium Hypochlorite comes into contact with microbes, it causes the denaturation of proteins within the cell. This denaturation is essentially a breakdown of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins, leading to a loss of function. For bacteria, this means that the enzymes critical for their metabolism and reproduction are rendered inactive, leading to cell death. Similarly, in fungi, the cell walls are compromised, disrupting their integrity and also leading to cell death.
For viruses, which are not cells but rather protein capsules with genetic material inside, bleach disrupts the capsid or outer protein coat. This destruction of the protective coat exposes the viral RNA or DNA, which then becomes a target for further degradation by the bleach. Without an intact capsid, viruses are unable to attach to and enter host cells, halting their replication process.
The oxidation process also targets the lipid membranes of certain pathogens, such as enveloped viruses, by reacting with the fatty acids in the lipids. This leads to the membrane’s rupture, spilling out the contents of the cell or virus and rendering it nonfunctional.
Additionally, Sodium Hypochlorite reacts with the nucleic acids of microorganisms. It can cause the fragmentation of the nucleotide chains, leading to the inactivation of the microbe’s genetic material. This prevents the microbe from performing vital functions like replication and protein synthesis, ultimately leading to cell death.
Sodium Hypochlorite’s ability to rapidly react and disrupt various structural components of pathogens makes it a highly effective disinfectant. This broad-spectrum activity, combined with its capacity to act quickly, has established Sodium Hypochlorite as a staple for disinfection protocols in various settings, including healthcare, water treatment, and, pertinent to our discussion, cannabis cultivation facilities, where maintaining a pathogen-free environment is crucial.
What are Viroids?
A viroid is a type of pathogen that is even simpler than a virus and is known to cause diseases in plants. Viroids consist of a short strand of circular, single-stranded RNA without a protein coat, which is a stark contrast to the more complex structure of viruses, which have a protein coat and often DNA or RNA as genetic material.
Here are the key characteristics of viroids:
- Size and Structure: Viroids are the smallest infectious pathogens known, consisting of a tiny RNA molecule that can range from a few hundred to a few thousand nucleotides in length. They do not have a protein coat (capsid) that typically encases viral genetic material.
- Replication: Viroids replicate within the host plant’s cells. They hijack the host cell’s machinery to synthesize new viroids. This process can interfere with the normal functioning of the plant’s cells, leading to symptoms of disease.
- Transmission: Viroids can be transmitted through mechanical means, such as contaminated tools, hands, and in some cases, through seed or pollen. They can also spread from plant to plant by contact.
- Symptoms: Infected plants may exhibit a range of symptoms including stunting, yellowing, leaf curling, and in severe cases, death of the plant. Symptoms depend on the type of viroid, the plant species, and environmental conditions.
- Host Range: Each viroid has a specific range of plant hosts that it can infect. Some viroids have a narrow host range, while others can infect a wide variety of plant species.
Viroids are a concern in agriculture and horticulture because they can cause significant crop losses and are difficult to control once they infect a plant population. There are no known chemical treatments that can cure a viroid infection; therefore, the focus is on prevention, quarantine, and eradication of infected plants to manage these pathogens.
Specific Viroids
Viroids are infectious pathogens that are even simpler than viruses, consisting solely of a short strand of circular RNA without a protein coat. They can cause diseases in plants, including cannabis. Here are some specific viroids known to affect cannabis plants:
- Hops Latent Viroid (HpLVd): This is the most commonly reported viroid in cannabis and hemp. It causes “dudding” or “stunting” disease, which leads to reduced vigor, stunted growth, brittle stems, abnormal flower development, and lower cannabinoid levels.
- Cannabis Cryptic Virus (CCV): While not a viroid, it’s worth mentioning as it is a virus that can also impact cannabis plants. It’s generally considered to be of low pathogenicity but can have synergistic effects with other pathogens.
Research on cannabis-specific viroids is still emerging, and given the similarities between cannabis and hops plants, viroids affecting hops are of particular concern for cannabis growers. However, the legal status of cannabis in many parts of the world has historically limited research, so the full spectrum of viroids that could potentially impact cannabis plants might not be fully documented yet.
It’s also important for growers to be aware of general plant viroids that could potentially cross-species barriers and affect cannabis plants, such as:
- Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid (PSTVd): A well-studied viroid that affects nightshade family plants, which could potentially be a risk if cannabis is grown in proximity to these species.
- Tomato Planta Macho Viroid (TPMVd): Known to affect tomatoes and other plants, it’s another example of a viroid that could be of concern in mixed agriculture settings.
Viroids are transmitted through mechanical means, such as contaminated tools or hands, and possibly through seed and pollen. Given the potential for significant crop loss, it is crucial for cannabis growers to implement strict sanitation measures to prevent the introduction and spread of these pathogens.

Daily and Weekly Routines: Your BLEACH Cultivation GUIDE
In the realm of cannabis cultivation, maintaining a sanitary environment is not just a good practice, it’s a cornerstone of success. Sodium hypochlorite, commonly known as bleach, is a critical component of this sanitization ritual. Here’s how to incorporate bleach into your daily and weekly cultivation routines.
Daily Diligence with Bleach
Morning Mist: Begin each day with a bleach-based misting solution. A diluted bleach mist can be gently sprayed on non-plant surfaces to address airborne pathogens that may have settled overnight. This should be done before the day’s cultivation activities commence to ensure a pristine starting environment.
Surface Swipes: Post-harvest activities can leave behind organic residues that are a calling card for microbial invaders. A daily wipe-down of all work surfaces with a bleach solution will keep these areas sterile. Pay special attention to tools, benches, trays, and any high-contact areas.
End-of-Day Overview: As the lights dim and the day’s cultivation work concludes, a final inspection with a bleach solution in hand will safeguard against any overlooked contaminants. Any spills or debris should be addressed immediately to prevent the attraction of pests or the incubation of mold spores.
Weekly Washing Wisdom
Deep Clean Dive: Once a week, take the time for a deeper cleaning session. This involves a more concentrated bleach solution and a thorough scrubbing of all surfaces, including floors, walls, and inaccessible nooks. It’s the time to be rigorous, ensuring that the week’s accumulation of potential pathogens is eradicated.
Equipment Examination: Your cultivation tools are indispensable allies in your growing process and deserve a weekly soak in a bleach solution. This will prevent the transfer of diseases from plant to plant and ensure that your equipment remains in optimal condition.
Irrigation Insights: For those employing hydroponic systems, your weekly routine should include flushing the system with a bleach solution. This prevents the buildup of algae and biofilm which can compromise plant health and system efficiency.
Ventilation Vigilance: Air circulation systems can harbor dust and mold. Weekly cleaning of filters and ducts with a bleach solution will prevent the circulation of unwanted particles and pathogens, contributing to a healthier grow space.
Safety Synopsis
While bleach is a potent ally, it must be handled with respect. Always wear protective gloves and ensure adequate ventilation when using bleach solutions. Additionally, never mix bleach with ammonia or other cleaners to avoid harmful fumes.
By adhering to these daily and weekly routines, your cultivation space remains a bastion of cleanliness, setting the stage for a bountiful and healthy harvest. Bleach, in its rightful place, becomes more than a cleaner; it’s a guardian of grow room sanctity.
Implementing these routines will help ensure that your cultivation space remains clean and productive. It’s important to note that the use of bleach must be managed carefully to prevent any harm to the plants or individuals applying the solution.
No ruler reigns alone in the Cannabis Realm, and Sodium Hypochlorite is no exception. It’s supported by a council of chemicals, each with its unique role to play.
Phosphoric Acid’s Role in Cannabis Cultivation
Phosphoric Acid plays a pivotal role in the cannabis cultivation industry, primarily as a pH down solution in nutrient mixes. In hydroponic systems, where precise pH control is essential for optimal nutrient uptake, phosphoric acid is a trusted agent to lower the pH level of nutrient solutions. Its efficacy is not just in pH adjustment; phosphoric acid also contributes phosphorus, a vital macronutrient, to the nutrient profile, supporting the development of strong roots and aiding in the flowering process. Additionally, as a cleaning agent, it can be used to remove mineral and rust deposits, ensuring that irrigation systems remain free from blockages and that the plants receive the clean water they need to thrive. Its dual role as a nutrient contributor and a cleaning agent underscores its indispensable value in the cannabis grower’s toolkit.
-
 Phosphoric Acid 30% – The Ultimate Rust Remover Solution$18.50 – $4,000.00
Phosphoric Acid 30% – The Ultimate Rust Remover Solution$18.50 – $4,000.00 -
 Phosphoric Acid 85% ACS Grade$31.00 – $6,480.00
Phosphoric Acid 85% ACS Grade$31.00 – $6,480.00 -
 Phosphoric Acid 85% USP Food Grade$25.00 – $6,615.00
Phosphoric Acid 85% USP Food Grade$25.00 – $6,615.00 -
 Phosphoric Acid 75%$24.00 – $5,670.00
Phosphoric Acid 75%$24.00 – $5,670.00 -
 Phosphoric Acid 85% – Technical Grade$29.00 – $6,075.00
Phosphoric Acid 85% – Technical Grade$29.00 – $6,075.00 -
 pH-Ree Fall – World Class Buffering Solution For PH Stability Made From Phosphoric Acid$18.00 – $4,000.00
pH-Ree Fall – World Class Buffering Solution For PH Stability Made From Phosphoric Acid$18.00 – $4,000.00
Isopropyl Alcohol’s Utility in the Cannabis Sphere
Isopropyl Alcohol, known for its disinfecting properties, is an essential supply in the cannabis industry’s arsenal. Its primary use is in the sterilization of cultivation tools and equipment, ensuring that every cut and interaction with the plant is free from contaminants that could introduce diseases to the crop. It’s also widely employed for cleaning resinous substances off harvesting tools and processing equipment, keeping them in pristine condition for handling the sticky trichomes of the cannabis plant. Beyond equipment maintenance, Isopropyl Alcohol serves as a quick-evaporating substance for sanitizing surfaces and is used in pest control strategies, where it can be applied to plants in a diluted form to combat certain pests without leaving harmful residues. In the meticulous world of cannabis cultivation, Isopropyl Alcohol’s versatility and effectiveness make it an indispensable component of daily operations.
-
 Isopropyl Alcohol 99.9% ACS Reagent Grade$22.00 – $3,600.00
Isopropyl Alcohol 99.9% ACS Reagent Grade$22.00 – $3,600.00 -
 Isopropyl Alcohol 70% USP Grade$25.00 – $3,700.00
Isopropyl Alcohol 70% USP Grade$25.00 – $3,700.00 -
 Isopropyl Alcohol 91%$21.00 – $3,300.00
Isopropyl Alcohol 91%$21.00 – $3,300.00 -
 Isopropyl Alcohol 99%$19.00 – $3,500.00
Isopropyl Alcohol 99%$19.00 – $3,500.00
Safety Guidelines for Using Bleach in Cannabis Cultivation Sanitization
Bleach, known chemically as Sodium Hypochlorite, is a powerful disinfectant used widely in cannabis cultivation to maintain a sanitary environment. While highly effective, it must be handled with care to ensure the safety of both the cultivator and the plants. Follow these safety guidelines when using bleach as a sanitization agent in your grow operations.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear appropriate PPE when handling bleach to protect your skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Gloves: Use gloves made of nitrile, rubber, or neoprene.
- Goggles: Wear safety goggles to prevent splash hazards.
- Respiratory Protection: Work in a well-ventilated area. Consider using a mask or respirator if ventilation is inadequate.
- Clothing: Protective clothing or aprons that are resistant to bleach.
Preparation and Mixing
Precision and caution are key when preparing your bleach solutions.
- Dilution: Only dilute bleach with water. The typical dilution ratio for sanitization is 1 part bleach to 9 parts water, but always refer to the label for specific instructions.
- Mixing: Add bleach to water, not water to bleach, to reduce the risk of chemical splashes.
- Containers: Use containers that are resistant to corrosion. Do not use metal containers as bleach can corrode metal.
Application
Apply bleach solutions safely to avoid damage to your plants and facility.
- Non-porous Surfaces: Apply on non-porous surfaces such as glass, plastic, and metal where pathogens are likely to reside.
- Avoid Plants: Do not apply bleach directly to cannabis plants. Bleach can be harmful and potentially lethal to plants.
- Controlled Application: Use sprayers or sponges for application to minimize aerosolization and drift.
Storage
Store bleach in a safe manner to prevent accidents and degradation of the product.
- Original Container: Keep bleach in its original container with labels intact.
- Cool and Dry: Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat to prevent degradation.
- Childproof: Ensure that storage areas are inaccessible to children and pets.
Disposal
Dispose of bleach solutions responsibly to safeguard the environment.
- Follow Regulations: Dispose of diluted solutions according to local regulations.
- Neutralization: Consider neutralizing highly concentrated bleach solutions before disposal.
Emergency Procedures
Be prepared for potential accidents.
- Eye Contact: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
- Skin Contact: If bleach comes into contact with skin, wash thoroughly with water. Remove contaminated clothing.
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air immediately if bleach fumes are inhaled. Seek medical attention if breathing difficulty occurs.
- Ingestion: If swallowed, do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water and seek medical attention immediately.
General Safety Tips
Additional tips to ensure a safe working environment.
- Never Mix Bleach with Ammonia or Acids: This can produce dangerous gases.
- Label Diluted Solutions: Clearly label all containers with diluted bleach solutions.
- Training: Ensure all personnel handling bleach are properly trained in its use and emergency response procedures.
Remember, safety is paramount in all aspects of cannabis cultivation. Proper handling and usage of bleach will ensure a clean and productive grow operation without compromising the well-being of the cultivator or the integrity of the plants.
These guidelines aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the safe use of bleach in a cannabis cultivation setting. They should be customized as needed to fit the specific requirements of your operation and local regulations.
The Chronicle of Clean: A Conclusion
Let’s be clear: maintaining an immaculate cultivation space is the cornerstone of successful cannabis production. It’s not just about what you see; it’s about what you can’t. Microscopic threats lurk where you least expect them, but armed with Sodium Hypochlorite and its chemical brethren, you’ll keep your grow room not just clean, but pristine.
In the end, the sanctity of your harvest depends on the vigilance of your sanitation practices. Embrace the routine, wield your chemicals wisely, and watch as your Cannabis kingdom thrives.