Toluene
An In-depth Look at Toluene
Toluene, also known by its systematic name methylbenzene, is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. A naturally occurring hydrocarbon, it’s an essential solvent and feedstock in the chemical industry.
Chemical Properties
Toluene (C7H8) belongs to the aromatic hydrocarbon class. It’s volatile, flammable, and has a distinctively sweet smell. It’s less dense than water and evaporates readily into the air.
Appearance and Odor
Being a clear liquid, toluene is recognized by its characteristic aromatic odor, which is often likened to that of paint thinners.
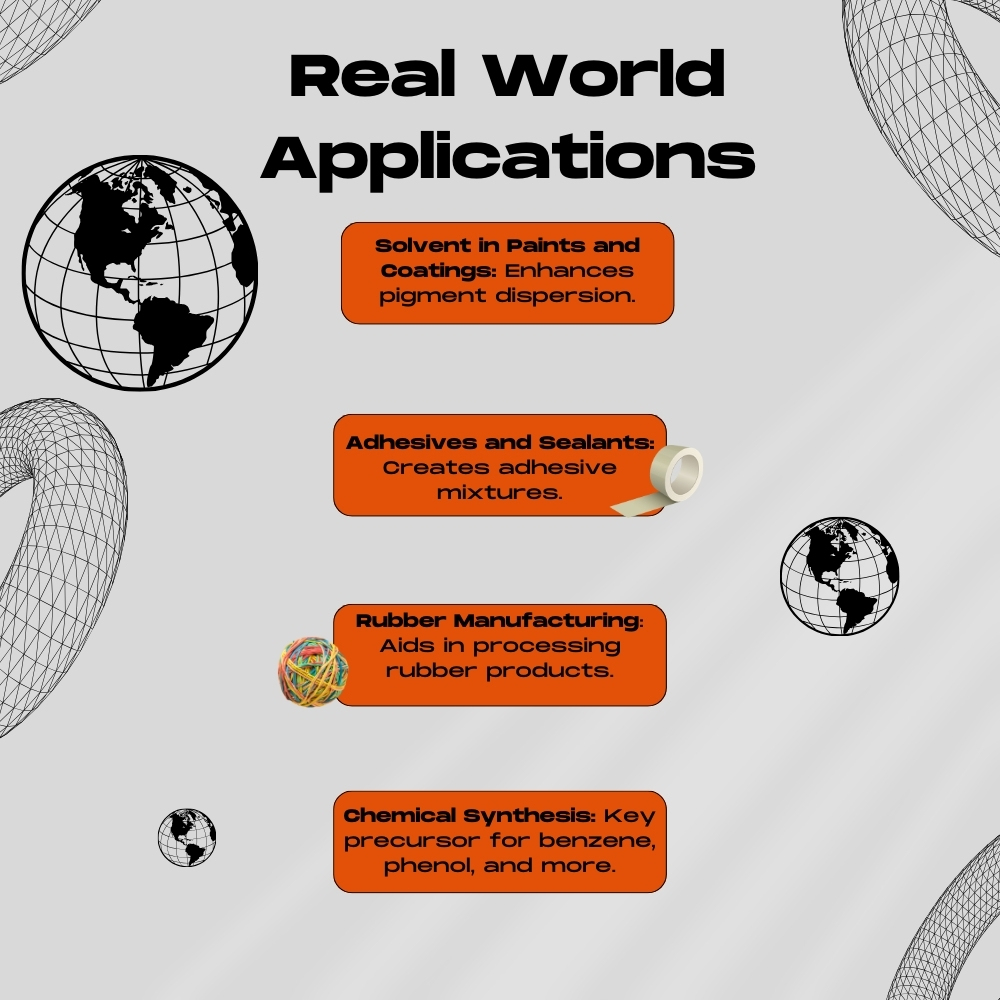
Principal Uses
Toluene’s versatile nature makes it a cornerstone in several industries.
Solvent Applications
Due to its ability to dissolve various compounds, it’s extensively used as a solvent in paints, rubber, printing ink, adhesives, and more.
Chemical Synthesis
It serves as a precursor to manufacture other chemicals, most notably benzene, xylenes, and a variety of synthetic drugs and explosives.
Fuel Addition
As an octane booster, toluene can be blended into gasoline to improve fuel’s anti-knock properties.
Handling and Safety
When working with toluene, adherence to safety protocols is paramount.
Protective Measures
Use in a well-ventilated area and wear protective gloves, eyewear, and clothing. Prolonged exposure can be harmful, so avoid inhalation and direct contact.
Storage Guidelines
It should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place, away from open flames or sparks. The container must be sealed tightly to prevent evaporation and inhalation risks.
Conclusion
While toluene is a critical component in various industries, its handling requires strict adherence to safety guidelines to mitigate health and environmental risks.